oxygen flow rate for pneumonia
Purpose of review. Management of oxygen supplementation is divided into nasal cannula and mechanical ventilation.
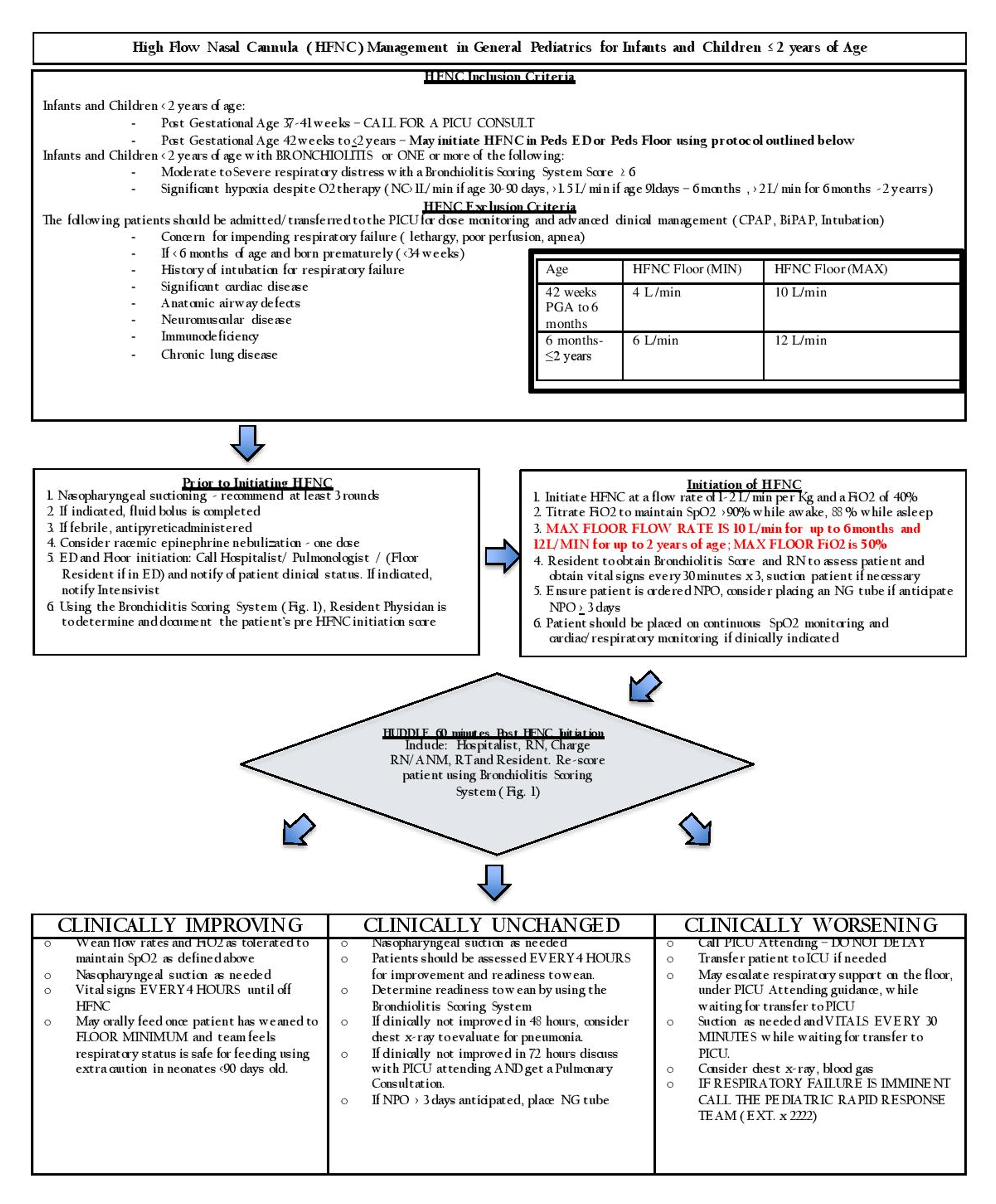
Cureus The Use Of High Flow Nasal Cannula And The Timing Of Safe Feeding In Children With Bronchiolitis
Depending on the patient oxygen saturation levels should be above 93 with the oxygen concentrations also varying depending on the patient their comorbidities and severity of pneumonia.

. Noninvasive ventilation is strongly advised for the treatment of hypercapnic respiratory failure. The WHO-recommended flow rates when using nasal prongs are 05 Lmin for young infants and 1 to 2 Lmin for preschool aged children with a maximum of 4 Lmin. On average flow rates of 06 to 10 Lmin are required to achieve 90 SpO 2 with high inter-patient variability.
After 6 h of HFNC oxygen therapy nonresponders presented a lower PaO 2 FiO 2 median 135 interquartile range 84210 versus 73 5661 mmHg p05 and needed a higher oxygen flow rate. It is not mentioned whether there was a subgroup of COVID-19 pneumonia patients treated with FiO2. No secondary infections were reported in health care workers.
Supplemental oxygen delivers to the lungs air that is 99 pure oxygen versus the air we normally breathe made up of about 20 oxygen. NHF is most commonly used oxygenating patients with severe acute respiratory failure from medical conditions such as pneumonia or bronchiolitis in children. Up to 100 humidified oxygen can be delivered at a high flow rate up to 60 Lmin that meets inspiration flow rates minimizing room air entrainment.
The reason they did not receive tocilizumab and why they were excluded from the study is also not explained. The provider sets the flow rate and Fi02. Mechanical ventilation is life-supporting ventilation that involves the use of a machine called a ventilator or respirator.
Another important aspect of pneumonia treatment is oxygen therapy and maintaining adequate oxygen saturation levels. We review the evidence on the use of noninvasive respiratory supports noninvasive ventilation and high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy in patients with acute respiratory failure because of severe community-acquired pneumonia. In many cases pneumonia patients whose symptoms are not life-threatening would be candidates to receive oxygen via an oxygen concentrator which is less expensive than a tank or cylinder.
Oxygen saturation 90 arterial oxygen partial pressure 60 mm Hg on room air or with low-flow supplemental oxygen via nasal cannula or return to. Oxygen supplementation is one way to help patients who cannot breathe adequately on their own.

Favipiravir Camostat And Ciclesonide Combination Therapy In Patients With Moderate Covid 19 Pneumonia With Without Oxygen Therapy An Open Label Single Center Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial Eclinicalmedicine

Tocilizumab Plus Dexamethasone Versus Dexamethasone In Patients With Moderate To Severe Covid 19 Pneumonia A Randomised Clinical Trial From The Corimuno 19 Study Group Eclinicalmedicine

High Flow Nasal Oxygen A Safe Efficient Treatment For Covid 19 Patients Not In An Icu European Respiratory Society

Pneumonia Bipap Secretions And Hfnc New Lessons From Florali
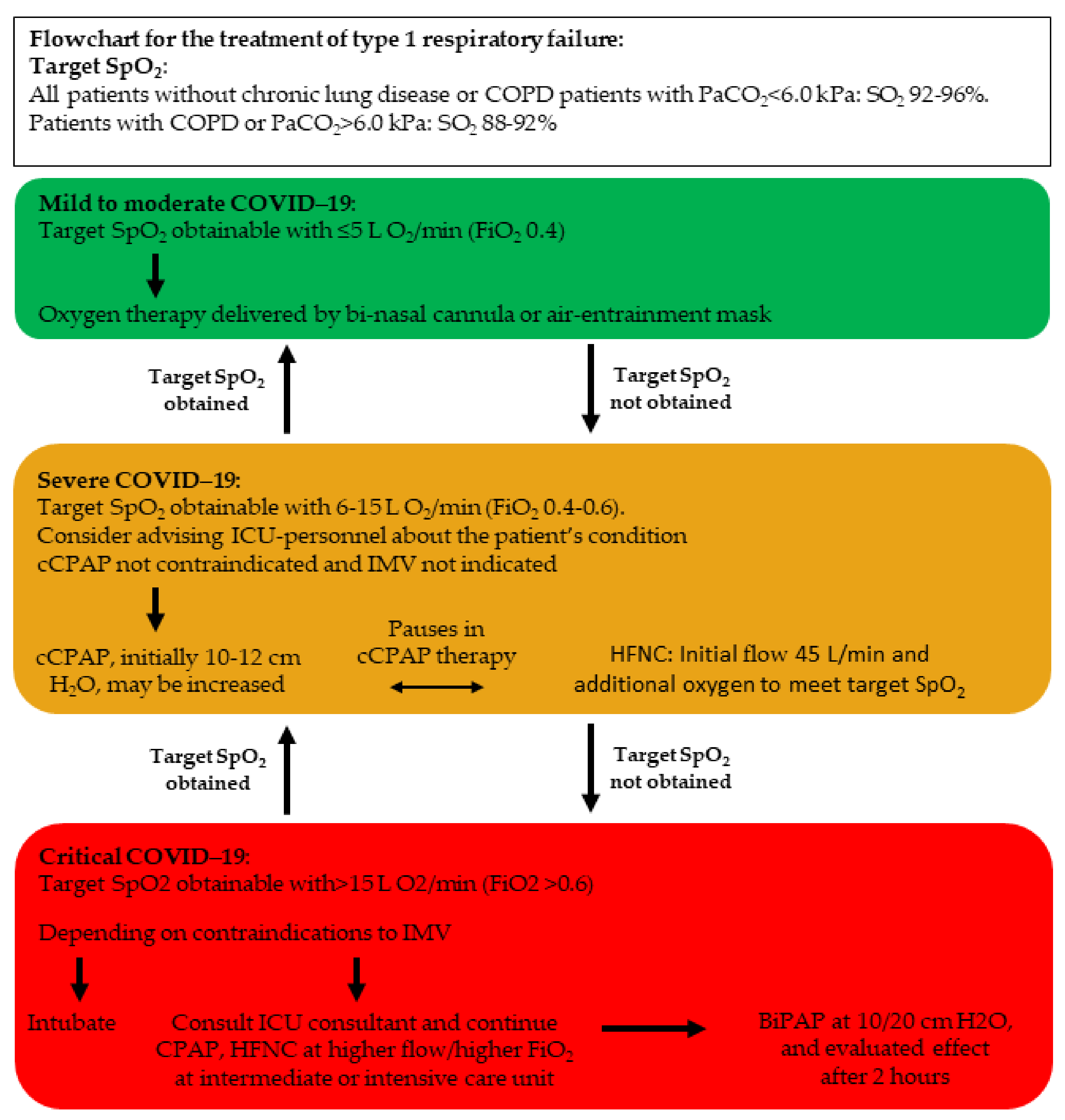
Diagnostics Free Full Text Management Of Covid 19 Associated Acute Respiratory Failure With Alternatives To Invasive Mechanical Ventilation High Flow Oxygen Continuous Positive Airway Pressure And Noninvasive Ventilation Html
Respiratory Support For Acute Intensive Care Clinician S Brief

Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy And Noninvasive

Effect Of High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy On Pediatric Patients With Congenital Heart Disease In Procedural Sedation A Prospective Randomized Trial Journal Of Cardiothoracic And Vascular Anesthesia

Pneumonia Bipap Secretions And Hfnc New Lessons From Florali
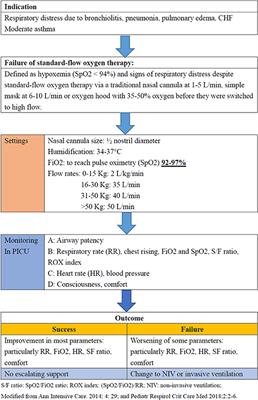
Frontiers High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy In Children With Acute Respiratory Distress With Hypoxia In A Pediatric Intensive Care Unit A Single Center Experience

Oxygen Therapy Nursing Pharmacology Osmosis

Molecular Profiling Of Innate Immune Response Mechanisms In Ventilator Associated Pneumonia Molecular Cellular Proteomics
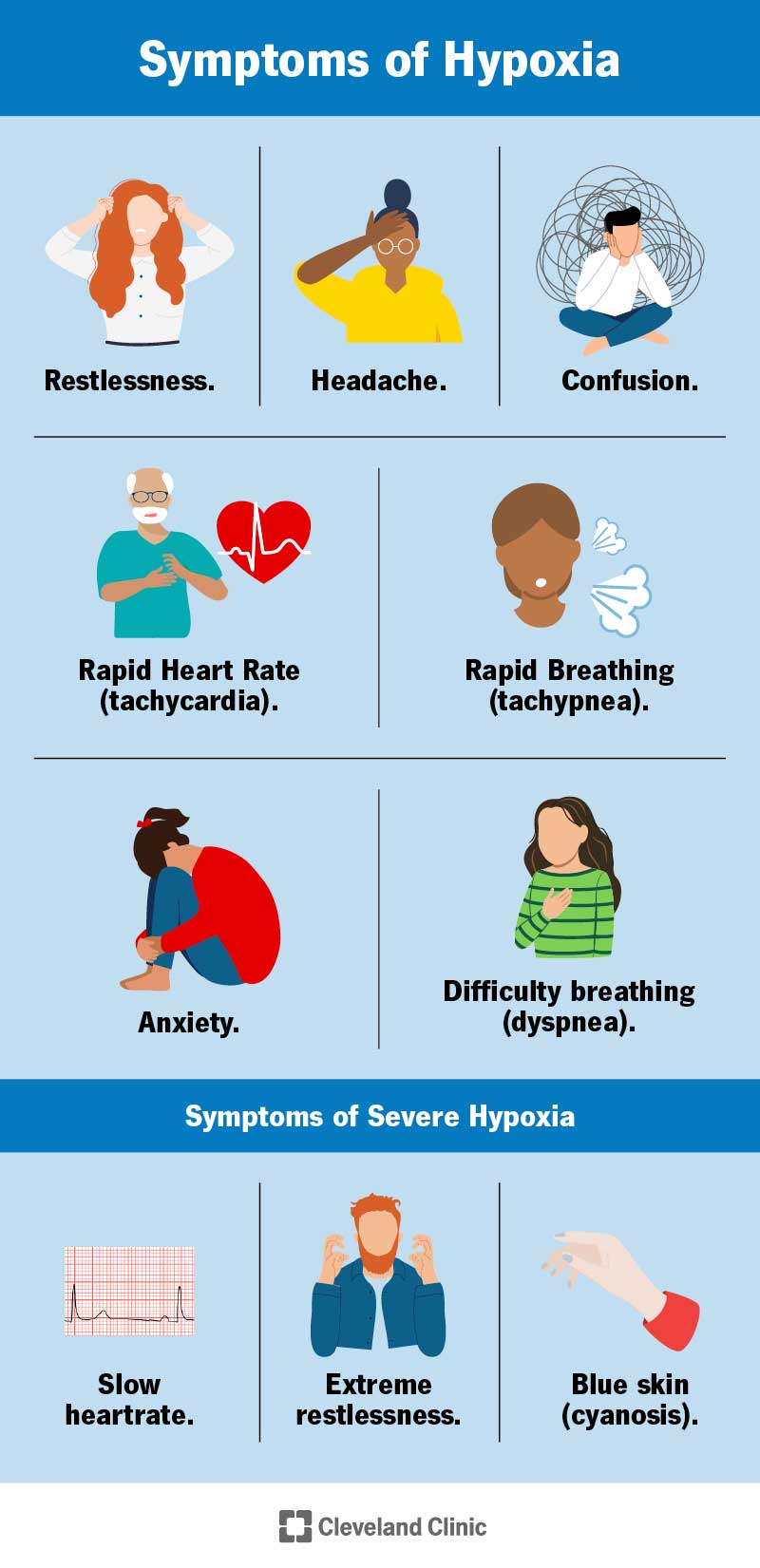
Hypoxia Causes Symptoms Tests Diagnosis Treatment

Predictive Factors Associated With High Flow Nasal Cannula Success For Covid 19 Related Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure Goury 2021 Health Science Reports Wiley Online Library

Assessment Of Pulmonary Arterial Circulation 3 Months After Hospitalization For Sars Cov 2 Pneumonia Dual Energy Ct Dect Angiographic Study In 55 Patients Eclinicalmedicine

Pneumonia Bipap Secretions And Hfnc New Lessons From Florali

Comparison Of Supplemental Oxygen Delivery By Continuous Versus Demand Based Flow Systems In Hypoxemic Copd Patients A Randomized Single Blinded Cross Over Study Respiratory Medicine

Providing Supplemental Oxygen To Patients Today S Veterinary Practice
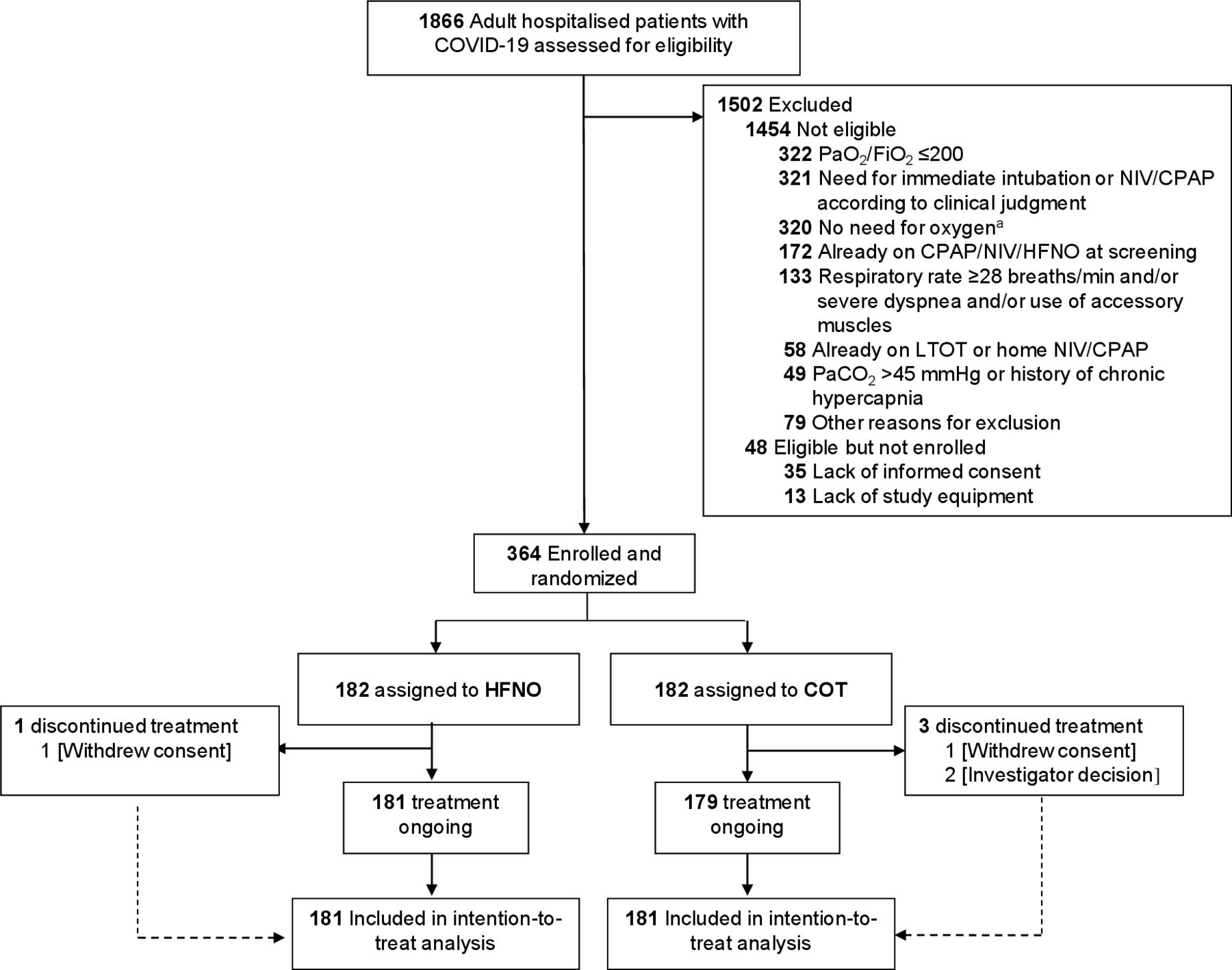
High Flow Nasal Oxygen Versus Conventional Oxygen Therapy In Patients With Covid 19 Pneumonia And Mild Hypoxaemia A Randomised Controlled Trial Thorax